|
Electromagnetically Induced Mixing of Glass Melt in a Pipe
This is a multiphysics electromagnetic stirring and mixing problem. The ADINA-EM  formulation and the ADINA CFD formulation are used, coupled, to simulate the advective mixing in an electromagnetically-driven pipe mixer. The schematic of this problem is as shown in Figure 6 below. In this example, fluid flows in a cylindrical tube subjected to stirring and mixing by the Lorentz force generated by time-dependent voltages in two electrodes that are immersed in the conducting fluid, with the entire assembly in an otherwise externally imposed constant magnetic field. Stirring and mixing occur in the plane perpendicular to the flow direction due to the Lorentz force in that plane. formulation and the ADINA CFD formulation are used, coupled, to simulate the advective mixing in an electromagnetically-driven pipe mixer. The schematic of this problem is as shown in Figure 6 below. In this example, fluid flows in a cylindrical tube subjected to stirring and mixing by the Lorentz force generated by time-dependent voltages in two electrodes that are immersed in the conducting fluid, with the entire assembly in an otherwise externally imposed constant magnetic field. Stirring and mixing occur in the plane perpendicular to the flow direction due to the Lorentz force in that plane.
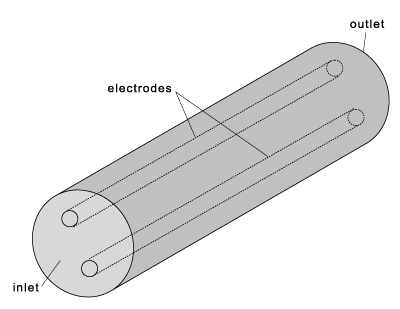
Figure 6 Electromagnetically induced mixing: schematic
The movie at the top shows the transient process of the mixing, starting from an inhomogeneous concentration at the inlet. In Figures 7 to 9 below, we present a steady-state solution of the electromagnetic mixing process, showing the calculated potentials 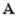 and and 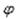 , the velocity in a plane perpendicular to the main flow direction, and the mass concentrations at the inlet and outlet. The homogeneous concentration at the outlet shows the perfect mixing achieved. , the velocity in a plane perpendicular to the main flow direction, and the mass concentrations at the inlet and outlet. The homogeneous concentration at the outlet shows the perfect mixing achieved.
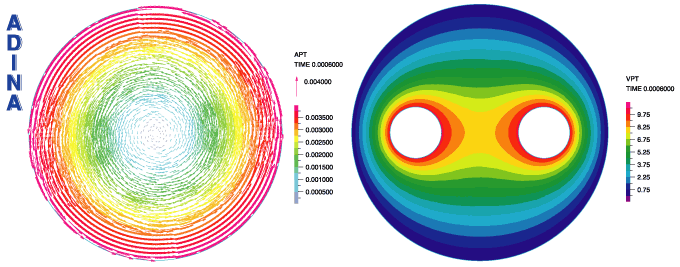
Figure 7 Electromagnetically induced mixing: Plot of  (left) and (left) and  (right) (right)
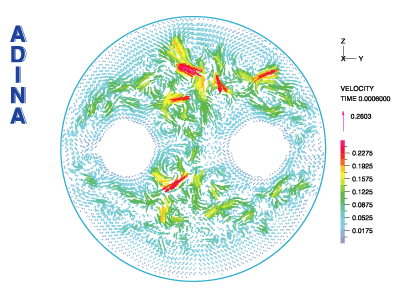
Figure 8 Electromagnetically (chaotic) induced mixing: velocity vector plot near inlet
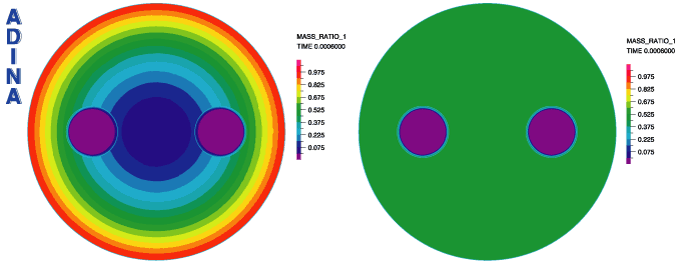
Figure 9 Electromagnetically induced mixing: mass ratio at inlet (left) and outlet (right)
Return to ADINA Electromagnetics Main Page
|





